고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
GPRS???
-
초고속 인터넷과 일부 영상통신이 가능한 2.5세대 이동전화
-
IMT-2000의 중간에 해당하는 기술이라 하여 2.5세대
-
3세대 이동통신의 실질적 서비스가 예상과 달리 늦춰질지 모른다는 우려에 새로운 대안으로 급부상
-
기존 2세대 이동전화보다 전송 속도가 10배 이상 빠름
-
패킷 교환기술을 이용해 언제든지 인터넷 등에 접속이 가능
-
GSM, UMTS, LTE core networks에서 사용되는 프로토콜 기반의 중요 IP/UDP 프로토콜
-
core네트워크를 통과할 때 user data를 encapsulate하고 다양한 core network entities간에 특정 bearer signaling traffic을 보낼 때 사용
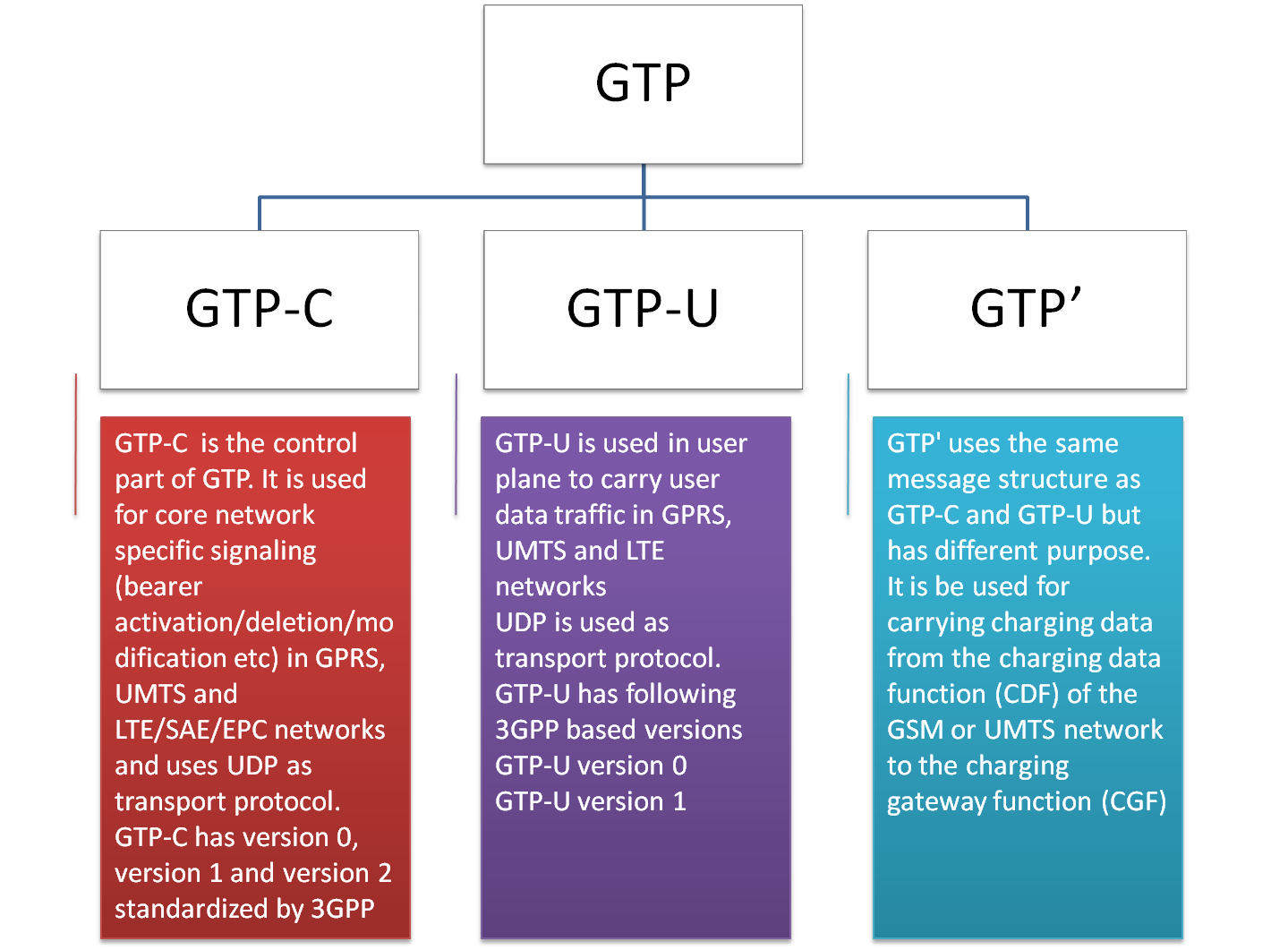
GPRS Tunneling Protocol Types
LTE에서 GTP 사용 이유
-
UE가 이동할 때 mobility를 제공하기 위해 IP 주소는 똑같이 남아 있고 packet은 SGW를 통해 PGW와 eNB, SGW 간에 tunneling을 할 때 계속 forwarding함
-
Multiple tunnels은 다른 네트워크 QoS를 얻기 위해 같은 UE에 의해 사용될 수 있음
-
Main IP 숨겨진 채로 남고 security를 제공
-
GTP-C의 경우 생성, 삭제, 터널 변형을 위해 사용
GTP interfaces in LTE

GTP-U 동작 원리
하향(DL): PDN(Internet)에서 UE 방향
1) 인터넷에서 P-GW로 패킷(Source IP=www.google.com, Destination IP=UE)이 수신됩니다.
2) P-GW는 수신한 패킷의 5-tuple (Source IP, Destination IP, Protocol ID, Source Port, Destination Port)을 자신이 가지고 있는 DL TFT과 비교하여(5-tuple 기반의 classification 수행) 어떤 EPS Bearer(GTP tunnel)에 본 패킷을 실어야 할 지 결정합니다. 이 말은, 각 UE별로 서로 구별되는 GTP tunnel이 있다는 말입니다. (정확히는 UE내에 응용별로 여러개의 GTP tunnel이 있을 수도 있음)
3) 어떤 EPS Bearer에 실어야 할지 알면 어떤 S-GW로, 어떤 "S5 TEID(DL)" 값을 적어서 보내야 할 지도 알게 됩니다. 그래서 P-GW는 S-GW로 (1) Outer IP header의 SIP=P-GW, DIP=S-GW로 하고, (2) GTP header에 S5 TEID(DL) 값을 실어서 GTP tunneling 패킷을 보냅니다.
S5 TEID(DL) 값은 UE가 망에 접속(Attach)시에 S-GW에서 생성하여 P-GW로 전달해 줍니다.
4) S-GW는 수신한 패킷의 "S5 TEID(DL)" 값을 참조하여 어떤 eNB로 보내야 할지와, 어떤 "S1 TEID(DL)" 값을 적어야 할지 알게 됩니다. 그래서 S-GW는 eNB로 (1) Outer IP header의 SIP=S-GW, DIP=eNB로 하고, (2) GTP header에 S1 TEID(DL) 값을 실어서 GTP tunneling 패킷을 보냅니다.
S1 TEID(DL) 값은 UE가 망에 접속(Attach)시에 eNB에서 생성하여 S-GW로 전달해 줍니다.
5) eNB는 수신한 패킷의 "S1 TEID(DL)" 값을 참조하여 어떤 UE로 보내야 할지와, 어떤 "DRB ID(DL)" 값을 적어야 할지 알게 됩니다. 그래서 eNB는 GTP tunnel header를 제거하고 UE에게 DRB ID(DL)을 적어서 패킷을 전달합니다.
상향(UL): UE에서 PDN(Internet) 방향
1) UE의 웹브라우저(응용프로그램)에서 www.google.com에 접속하려 합니다.
2) UE는 UL TFT를 통해서(UL TFT 값은 UE가 LTE 망에 접속하면서 망으로 부터 받습니다) 본 패킷을 어떤 EPS Bearer를 통해 보낼지 결정합니다(UL TFT 역시 5-tuple 기반으로 패킷을 분류하여 EPS Bearer를 결정)
3) 어떤 EPS Bearer에 실어야 할지 알면 어떤 eNB로, 어떤 "DRB ID(UL)" 값을 실어서 보내야 할지 알게 됩니다. eNB로 DRB ID를 추가하여 패킷을 보냅니다.
4) eNB는 수신한 패킷의 "DRB ID(UL)" 값을 참조하여 어떤 S-GW로, 어떤 "S1 TEID(UL)" 값을 적어서 보내야 할지 알게 됩니다. 그래서 eNB는 S-GW로 (1) Outer IP header의 SIP=eNB, DIP=S-GW로 하고, (2) GTP header에 S1 TEID(UL) 값을 실어서 GTP tunneling 패킷을 보냅니다.
S1 TEID(UL) 값은 UE가 망에 접속(Attach)시에 S-GW에서 생성하여 eNB로 전달해 줍니다.
5) S-GW는 수신한 패킷의 "S1 TEID(UL)" 값을 참조하여 어떤 P-GW로, 어떤 "S5 TEID(UL)" 값을 적어서 보내야 할지 알게 됩니다. 그래서 S-GW는 P-GW로 (1) Outer IP header의 SIP=S-GW, DIP=P-GW로 하고, (2) GTP header에 S5 TEID(UL) 값을 실어서 GTP tunneling 패킷을 보냅니다.
S5 TEID(UL) 값은 UE가 망에 접속(Attach)시에 P-GW에서 생성하여 S-GW로 전달해 줍니다.
6) P-GW는 수신한 패킷의 "S5 TEID(UL)" 값을 참조하여 어떤 UE가 보낸 패킷인지 압니다. 이후 GTP tunnel header를 제거하고 인터넷으로 패킷을 보냅니다.

GTP-C signaling messages
As GTP-Cv2 in LTE is used for tunnel management, some of the signalling messages are listed below which use GTP-Cv2 protocol

용어 정리
-
MME (Mobility Management Entity): The MME is the key control-node for the LTE access-network. It is responsible for idle mode UE (User Equipment) paging and tagging procedure including retransmissions. It is involved in the bearer activation/deactivation process and is also responsible for choosing the SGW for a UE at the initial attach and at time of intra-LTE handover involving Core Network (CN) node relocation. It is responsible for authenticating the user (by interacting with the HSS). The Non Access Stratum (NAS) signaling terminates at the MME and it is also responsible for generation and allocation of temporary identities to UEs. It checks the authorization of the UE to camp on the service provider’s Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) and enforces UE roaming restrictions. The MME is the termination point in the network for ciphering/integrity protection for NAS signaling and handles the security key management. Lawful interception of signaling is also supported by the MME. The MME also provides the control plane function for mobility between LTE and 2G/3G access networks with the S3 interface terminating at the MME from the SGSN. The MME also terminates the S6a interface towards the home HSS for roaming UEs.
-
SGW (Serving Gateway): The SGW routes and forwards user data packets, while also acting as the mobility anchor for the user plane during inter-eNodeBhandovers and as the anchor for mobility between LTE and other 3GPP technologies (terminating S4 interface and relaying the traffic between 2G/3G systems and PGW). For idle state UEs, the SGW terminates the downlink data path and triggers paging when downlink data arrives for the UE. It manages and stores UE contexts, e.g. parameters of the IP bearer service, network internal routing information. It also performs replication of the user traffic in case of lawful interception.
-
PGW (PDN Gateway): The PDN Gateway provides connectivity from the UE to external packet data networks by being the point of exit and entry of traffic for the UE. A UE may have simultaneous connectivity with more than one PGW for accessing multiple PDNs. The PGW performs policy enforcement, packet filtering for each user, charging support, lawful interception and packet screening. Another key role of the PGW is to act as the anchor for mobility between 3GPP and non-3GPP technologies such as WiMAX and 3GPP2 (CDMA 1X and EvDO).
-
HSS (Home Subscriber Server): The HSS is a central database that contains user-related and subscription-related information. The functions of the HSS include functionalities such as mobility management, call and session establishment support, user authentication and access authorization. The HSS is based on pre-Rel-4 Home Location Register (HLR) and Authentication Center (AuC).
-
ANDSF (Access Network Discovery and Selection Function): The ANDSF provides information to the UE about connectivity to 3GPP and non-3GPP access networks (such as Wi-Fi). The purpose of the ANDSF is to assist the UE to discover the access networks in their vicinity and to provide rules (policies) to prioritize and manage connections to these networks.
-
ePDG (Evolved Packet Data Gateway): The main function of the ePDG is to secure the data transmission with a UE connected to the EPC over an untrusted non-3GPP access. For this purpose, the ePDG acts as a termination node of IPsec tunnels established with the UE.
EPS bearer
SDF(Service Data Flow)
Ref
[1] GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) in LTE, http://4g-lte-world.blogspot.kr/2013/03/gprs-tunneling-protocol-gtp-in-lte.html
[2] GPRS, http://terms.naver.com/entry.nhn?docId=1213098&cid=40942&categoryId=32848
'Streaming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| nginx를 이용한 스트리밍 서버(빌드 및 설치) (0) | 2020.03.25 |
|---|---|
| nginx + hls 스트리밍(vod 파일 이용) (0) | 2020.02.03 |
| GoP(Group of Pictures) (0) | 2019.07.12 |





댓글 영역